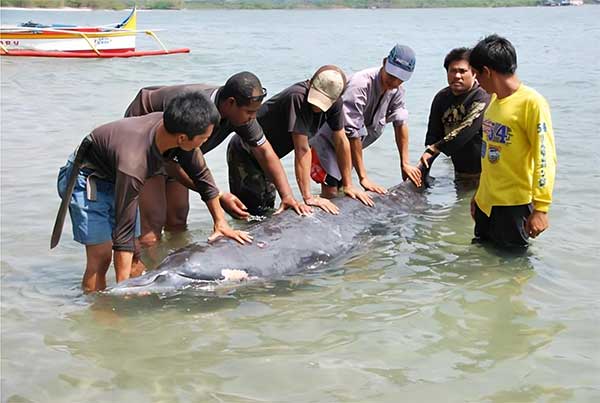
With a significant number of marine mammals stranded in the Philippines over the past years, it is within the scope of local government units (LGUs) to address this pressing concern, scientists from the University of the Philippines – Diliman College of Science (UPD-CS) indicated in a recent study that encompasses data from the past almost two decades.

Dr. Lemnuel Aragones, Alessandra Nicole Morado, and Honey Leen Laggui of the Institute of Environmental Science & Meteorology (IESM), along with Dr. Marie Christine Obusan of the Institute of Biology (IB), Dr. Jonah Bondoc of the Natural Sciences Research Institute (NSRI), and Dr. Leo Suarez of Ocean Adventure and Ewen Lawler of University of Canberra, assessed the changes in marine mammal strandings in the Philippines over space and time, as well as the types of species that got stranded in Philippine territory from 2005 to 2022.
Marine mammal strandings and the role of LGUs
A marine mammal stranding occurs when a marine mammal is found on seashores or in shallow waters and cannot return to deeper waters on its own. The researchers mapped the stranding hotspots in the Philippines, representing areas where standing frequencies are relatively high, and designed the hotspots to identify designated LGUs to inform them about the implications of the strandings for marine mammal conservation and management. With the help of the hotspots, concerned LGUs can also be proactive in addressing marine mammal strandings. A total of 35 LGU hotspots for strandings were identified in this study. The majority of these stranding hotspots were located in Luzon (with 24 hotspots), particularly in Regions 1 and 2.
“Strandings can be of natural causes, but when marine mammals with good body condition strand, we have to worry because it could imply that they are in trouble. It is possible that their habitat is compromised in various ways – most likely from human activities such as pollution and overexploitation of our key marine resources,” explained Dr. Aragones, who also serves as the president of the Philippine Marine Mammal Stranding Network (PMMSN).
While natural causes such as tropical monsoons and oceanographic factors can affect marine mammal strandings, the study emphasized that fisheries production and fisheries interaction are major contributors to the stranding frequencies of these mammals. This can occur through fishing equipment that increases the chances of entanglement or various illegal fishing activities, such as dynamite fishing.
“We recommend that LGUs and concerned regional offices establish their own stranding response team and rehabilitation tank and eradicate illegal fishing activities in their area by providing appropriate crew and patrol boats,” the researchers stated in their study. They also emphasized the importance of information, education, and communication (IEC) campaigns regarding marine mammals and regulating fishers and their fishing gear. By institutionalizing these programs, LGUs and concerned regional offices will help sustain their implementation.

Their study also revealed that the species most frequently stranded in Philippine waters were spinner dolphins (Stenella longirostris) with 218 strandings, dugongs (Dugong dugon) with 104 strandings, Risso’s dolphins (Grampus griseus) with 100 strandings, Fraser’s dolphins (Lagenodelphis hosei) with 95 strandings, and melon-headed whales (Peponocephala electra) with 89 strandings. By establishing a ‘species stranding status,’ an index of the impacts of stranding on these already vulnerable and endangered species, this study has introduced an important additional key factor in assessing species conservation status by concerned agencies.
Generating more research on stranded marine mammals
Knowing the species—particularly identifying their genetics and genomics—is important for ensuring the proper management of stranded marine mammals. This is the focus of the new ongoing studies by Dr. Aragones and his colleagues.
“We should determine the main causes of strandings. Since we suspect that dynamite blasts can cause strandings, we want to understand the acoustics of marine mammals,” elaborated Dr. Aragones. “We also like to examine the impact of fisheries on our marine mammals, to identify what types of fishing gears can entangle them, and the bycatch rates as well.”
Their findings underscore the importance of continuing and advancing monitoring efforts for marine mammal strandings, given the inevitable impacts of human activities such as increasing population, illegal fishing, pollution, and climate change. The evidence-based results provided by this study can guide stranded hotspot LGUs and concerned regional offices in managing and conserving Philippine marine resources, including marine mammals.
References:
Aragones, L. V., Morado, A. N., Obusan, M. C., Laggui, H. L., Bondoc, J. L., Suarez, L. J., & Lawler, E. K. (2024). Spatiotemporal variation of stranded marine mammals in the Philippines from 2005 to 2022: Latest stranding hotspots and species stranding status. Aquatic Mammals, 50(4), 302-322. https://doi.org/10.1578/am.50.4.2024.302