By Francis Allan L. Angelo
Major crop production in Western Visayas for the third quarter of 2024 revealed a mixed performance, with coconut remaining the region’s top crop despite a slight decline in output, according to data from the Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA).
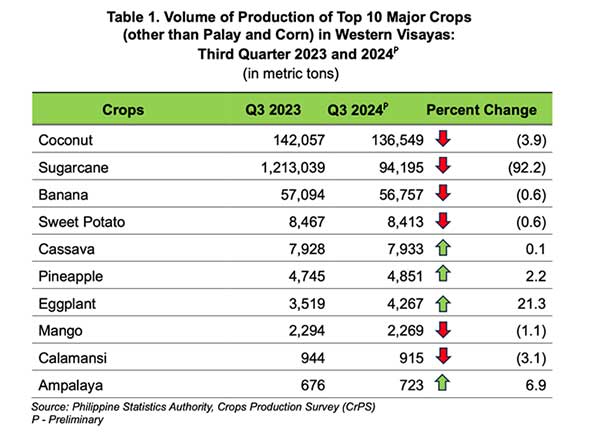
Coconut production topped the region’s major crops with a volume of 136,549 metric tons. However, this marked a 3.9 percent decline compared to the same period in 2023, when production was 142,057 metric tons.
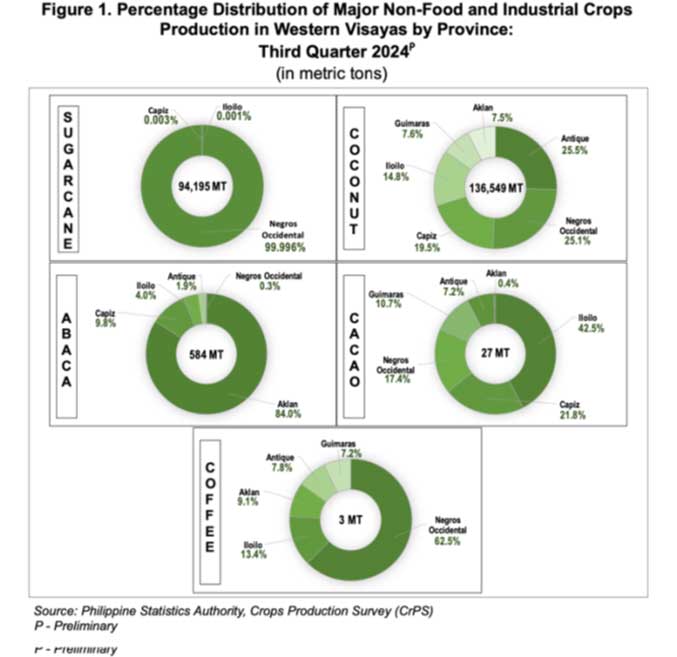
The crop remains a crucial part of the regional agricultural landscape, with Antique contributing 25.5% of the production, followed by Negros Occidental (21.5%), Capiz (19.5%), and Iloilo (14.8%).
Aklan and Guimaras shared the remaining 16 percent almost equally.
Sugarcane Suffers Major Blow
The coconut sector’s performance aligns with the broader challenge of declining output in key crops such as sugarcane, which experienced a dramatic 92.2 percent drop in production, falling from 1.2 million metric tons in Q3 2023 to just 94,195 metric tons in Q3 2024.
Negros Occidental, the region’s top sugarcane producer, accounted for nearly all the production, with a share of 99.996%.
Fruits and Vegetables Show Mixed Results
Western Visayas’ fruit crops saw mixed results. Banana production totaled 56,757 metric tons, a slight dip of 0.6% compared to 57,094 metric tons last year. Negros Occidental led the banana harvest with 46.2% of the total, followed by Iloilo at 27.3%.
Conversely, pineapple production rose by 2.2% to 4,851 metric tons, with Iloilo contributing 67.2% and Negros Occidental 28.6%. Mango production also declined marginally by 1.1% to 2,269 metric tons, while calamansi recorded a 3.1% decrease to 915 metric tons.
Among vegetable and root crops, eggplant emerged as a standout, with a 21.3% increase in production to 4,267 metric tons, primarily driven by Iloilo, which contributed 70.2%. Ampalaya (bitter gourd) also rose by 6.9%, while sweet potato production slightly declined by 0.6% to 8,413 metric tons, with Negros Occidental providing the largest share at 51%.
Cassava Holds Steady Amid Declines
Cassava production showed stability, growing by a marginal 0.1% to 7,933 metric tons. Negros Occidental led regional production with 48.4%, while Capiz and Antique contributed 23.2% and 10.9%, respectively.
Iloilo Leads Regional Diversity
Iloilo emerged as a significant contributor across various crop categories, leading in mango, pineapple, and calamansi production while ranking second in banana. It also dominated vegetable and root crop production, particularly eggplant and tomato, with shares exceeding 70% for both crops.


















