By Francis Allan L. Angelo
A new report by Fortinet highlights the persistent cybersecurity skills shortage in the Philippines, revealing that 94% of organizations experienced at least one security breach in the past year, with many attributing these incidents to a lack of adequate cyber skills.
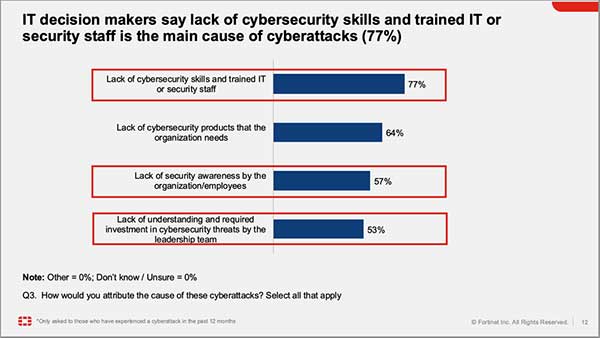
The 2024 Global Cybersecurity Skills Gap Report underscores the growing urgency for organizations to address this issue, as 77% of surveyed leaders believe the skills gap is increasing cyber risks for their companies.
“As the skills shortage persists, this leading cybersecurity challenge requires a collaborative, multi-faceted approach,” said John Maddison, Chief Marketing Officer at Fortinet.
“This year’s report emphasizes that for organizations to ensure they are protected from today’s complex threats, they must have a combination of the right security technology, opportunities for current security professionals to upskill, and an overall cyber-aware workforce.”
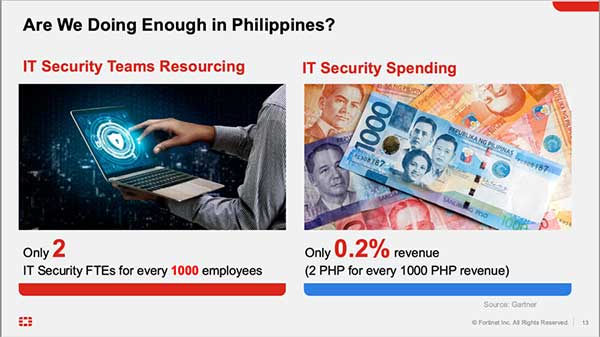
The report, which surveyed 25 IT and cybersecurity decision-makers across various industries in the Philippines, paints a concerning picture of the local cybersecurity landscape.
Not only are breaches becoming more frequent, but they are also more costly—52% of organizations reported that breaches cost them over $1 million in the past year, up from 45% in 2023.
Alan Reyes, Country Manager at Fortinet Philippines, emphasized the critical need for ongoing efforts to close the skills gap.
“More organizations are increasingly linking security breaches to the cybersecurity skills gap, with 94% of organizations in the Philippines recognizing this issue, up from 92% in the last report. This emphasizes the urgent need for organizations in the Philippines to continue addressing the cybersecurity skills shortage to strengthen their security posture,” Reyes said.
The findings also show that corporate leaders are facing personal repercussions when breaches occur.
Sixty-two percent of respondents indicated that executives or board members have faced fines, jail time, or loss of position following a cyberattack.
Moreover, the report found that 94% of organizations consider cybersecurity a top business priority, a clear indication of its critical role in today’s business environment.
The report also highlights the value of certifications in addressing the skills gap. A significant 94% of respondents prefer to hire candidates with certifications, and 98% are willing to pay for their employees to obtain these credentials.
However, finding candidates with the necessary certifications remains a challenge, as 84% of respondents noted difficulty in this area.
To mitigate these challenges, many organizations are diversifying their recruitment efforts, with 88% setting diversity hiring goals.
Additionally, companies are increasingly focusing on a three-pronged approach to building cyber resilience: investing in training and certifications, cultivating a cyber-aware workforce, and deploying effective security technologies.





















