By Edwin Concepcion
Innovations in the last decade such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) have revolutionised industries, creating new avenues for productivity, growth and insight-generation. While such technological endeavour has paved the way for transformative breakthroughs, it has also expanded the challenges of safeguarding data privacy. It is now more critical than ever that we become adept at balancing the value of cutting-edge technology with taking data protection measures against those who seek to extract and exploit personal information from new vulnerabilities.
Impact of Innovations on Data Privacy and the Rise of New Threats
While smart devices that seamlessly integrate into our lives offer unparalleled convenience, they also very often collect vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns on how this information is processed, stored, used and shared. Present in our homes and carried on ourselves, multi-device connectivity and data-sharing has further amplified security risks for unsecure devices that can serve as gateways for hackers to infiltrate networks with zero-day vulnerabilities.
In a recent article published on the Data Protection Excellence (DPEX) Network, we spoke about how integrating a company’s data with Generative AI services like ChatGPT or any other provider can introduce security and privacy vulnerabilities as it involves sharing data with external providers. The extent of these risks hinges on various factors, including the provider’s reputation, data handling policies, and alignment with data protection regulations such as purpose of use. But whether the service provider may be considered to be compliant depends on the regulations that they are subject to, such as the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) in Singapore or the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Economic Area Union (EEA).
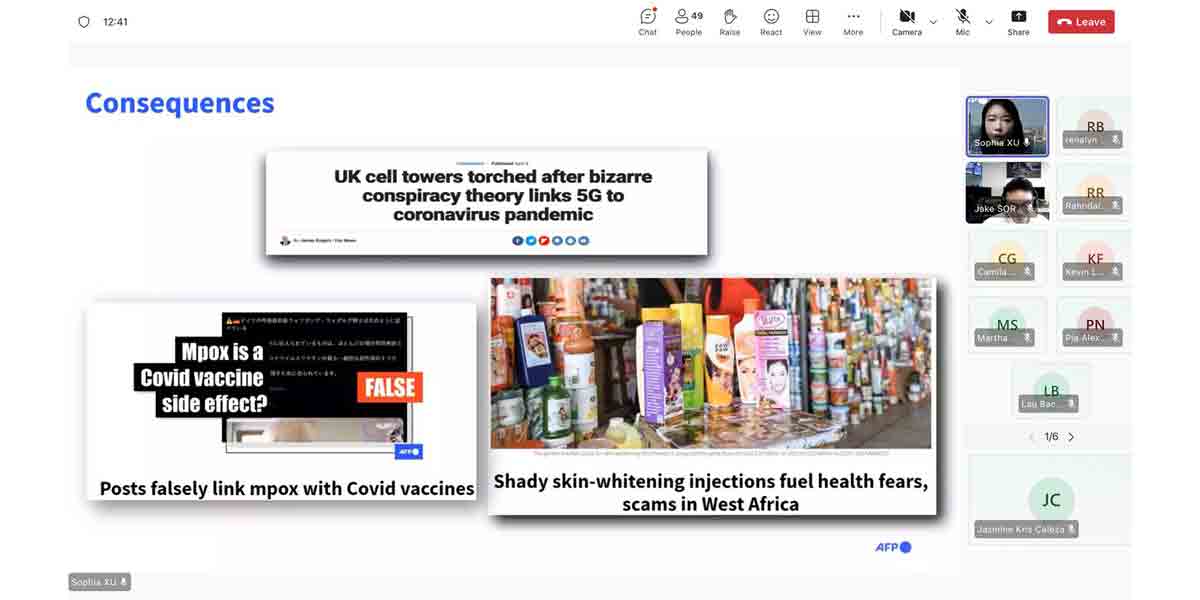
While AI is being adopted by entities with positive intentions of boosting workforce productivity, malicious actors have also tapped into the technology to create cyberattacks that are reaching new levels of sophistication. Last month, Netenrich’s threat research team found FraudGPT, a new subscription-based Generative AI tool sought out by hackers in the dark web that can craft convincing phishing strategies of uncanny realism. According to Netenrich, FraudGPT can write malicious code, create undetectable malware, phishing pages, hacking tools and write scam pages or letters.
The advancement of social engineering scams, driven by Generative AI, corresponds to a surge in ransomware incidents from victims clicking on malicious attachments and webpages, resulting in them having their data held hostage by hackers. Such rise in cyberattacks underscores the need for comprehensive data protection strategies and processes. Organisations must adopt a proactive stance, combining technical safeguards with ongoing employee education to fortify their digital defences.
Nurturing Trust Amidst Technological Experimentation
As the technology of an organisation evolves, so do its vulnerabilities. By subjecting software systems to comprehensive scrutiny before implementation, organisations can identify and address potential data privacy and security gaps. However, maintaining client trust throughout this process is equally important.
Transparent communication about data collection and usage, coupled with robust opt-in mechanisms, ensures that users remain informed and confident that their personal data is kept safe and used only for specific purposes. As a further step to assure users of the organisation’s data privacy compliance and cross-border data transfers in technological transitions, businesses and government agencies in the Philippines may pursue the Philippine Privacy Trust Mark (PPTM) by the National Privacy Commission (NPC). According to former NPC commissioner Raymund Liboro, with the PPTM, data subjects are able to make better-informed choices and have more control over their own personal data in the hands of organisations.
When it comes to cloud integrations, implementing strong network segmentation and regularly updating IoT firmware can significantly reduce vulnerabilities for an organisation and their customers’ data. As a mark of assurance to clients, the organisation should conduct regular network vulnerability security scans to assess for possible gaps within the IT infrastructure and ensure that these issues are fixed as quickly as possible to maintain trust with data subjects.
Due diligence in organisations must be done before embarking on integrating AI services like ChatGPT, thoroughly evaluating the Generative AI provider’s policies and practices. For instance, ChatGPT differentiates between its API consumer services and non-API version. By grasping these distinctions, the organisation can make informed decisions regarding data sharing and usage.
Organisations acting as data controllers should also expect a range of data privacy measures from the Generative AI service providers they are seeking to use, so as to ensure their client’s data security and compliance with relevant data protection regulations in the country. If the organisation is the Philippines, then the Generative AI service provider should be in alignment with the four General Data Privacy Principles of the Philippine Data Privacy Act (DPA) – Transparency, Legitimate Purpose, Proportionality, and Accountability – which govern the way organisations collect, use, and store personal data. Further, the DPA details eight rights of data subjects that must be upheld by Personal Information Controllers (PICs) and Personal Information Processors (PIPs). As an organisation deals with personal data of their clients and staff, this must be taken into consideration when evaluating the suitability of third-party vendors too.
Navigating the Jurisdictional Maze: Varied Data Laws and User Experience
At the same time, varying data laws across jurisdictions introduce a unique layer of complexity. Businesses operating across multiple regions must tread carefully, navigating a patchwork of regulations to ensure a seamless and compliant user experience.
By assessing risk tolerance and aligning with relevant data protection regulations such as the DPA in the Philippines, PDPA in Singapore or GDPR in the EEA, companies can ensure a secure environment for themselves and their clients. These safeguards include obtaining consent, limiting data usage, cross-border compliance, and controlled data sharing with external entities.
Conclusion: Forging Ahead with Innovation and Protection
The rapid pace of technological advancement poses opportunities for increasing business efficiency but at the same time poses challenges for data protection. As we embrace innovation, we must simultaneously cultivate robust strategies that safeguard the trust of our clients and users. Our journey into the digital future is uncertain, but with a steadfast dedication to comprehensive data protection, we can ensure that technology, privacy, and innovation can flourish hand in hand.
The author is the Philippine Country Manager of Straits Interactive